Dual Agonist
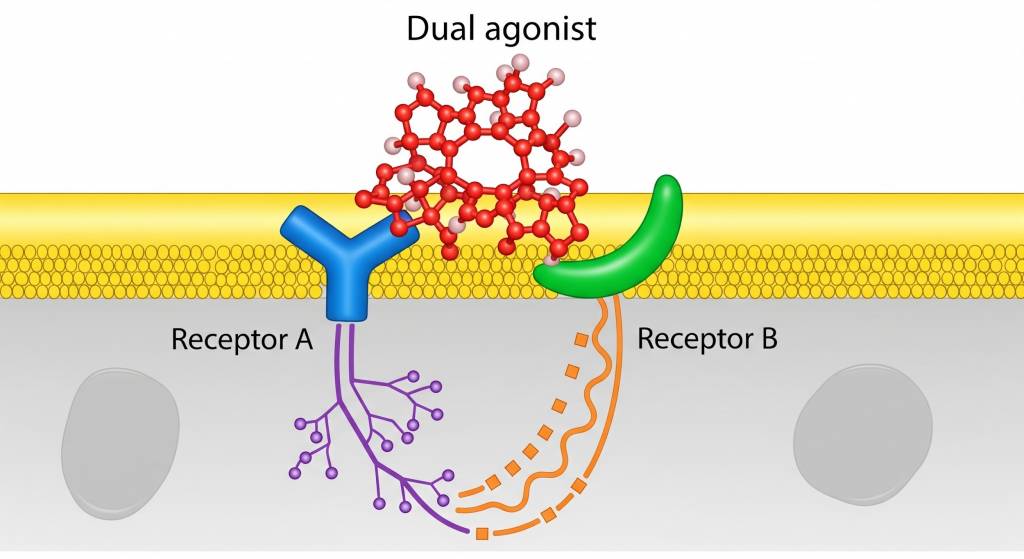
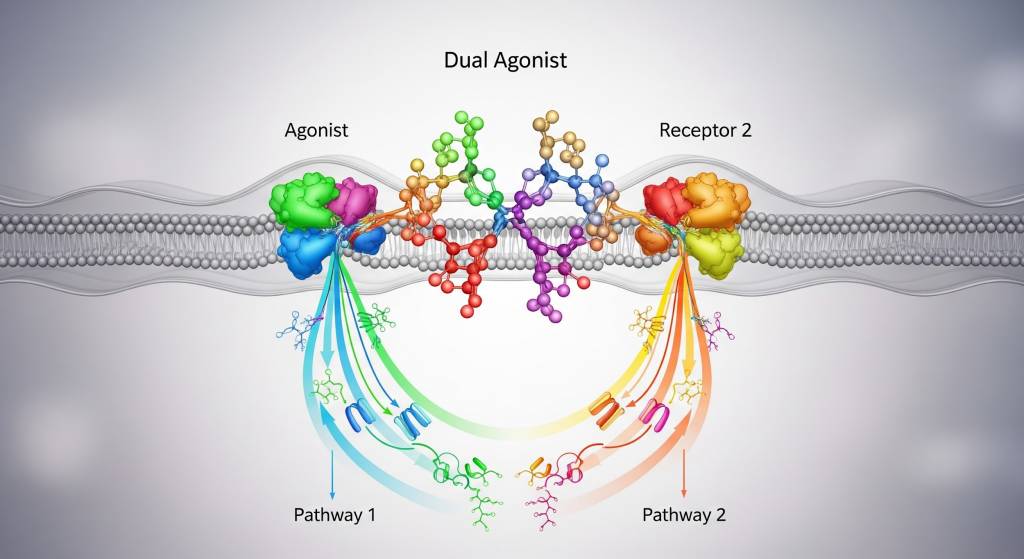
A dual agonist refers to a single signaling molecule or compound that activates two distinct biological receptors or signaling pathways simultaneously. In biological and peptide research, dual agonists are studied to understand how coordinated receptor activation influences complex physiological processes, such as metabolic regulation, neuroendocrine signaling, or immune coordination.
Unlike single-pathway agonists, dual agonists allow researchers to investigate integrated signaling effects that more closely reflect how biological systems operate in interconnected networks.
⚠️ Research Disclaimer:
This content is provided strictly for educational and research purposes. No information on this page constitutes medical advice, dosing guidance, or instructions for human or animal use.
Research Context
In research settings, dual agonists are examined to explore:- Synergistic effects between two receptor pathways
- Cross-talk between signaling systems
- Amplification or modulation of biological responses
- Improved signaling efficiency compared to single agonists
- System-level regulation rather than isolated pathway effects
Dual Agonists in Metabolic Research
From a metabolic research perspective, dual agonists are commonly studied in relation to:- Appetite regulation signaling
- Glucose and insulin-related pathways
- Energy expenditure coordination
- Gut–brain communication systems
Relevance to Peptide Research
Dual agonists are highly relevant to peptide research because peptides can be engineered or selected to:- Bind selectively to multiple receptors
- Coordinate complementary signaling pathways
- Reduce signaling redundancy
- Provide insight into multi-pathway regulation
Related Research Compounds
Dual agonist signaling is commonly referenced in research involving peptides such as:- Tirzepatide – studied for dual incretin pathway activation
- Cagrilintide – examined in appetite and metabolic signaling research
- Retatrutide – researched for integrated metabolic signaling pathways
Related Glossary Terms
- Tri-Agonist
- GLP-1 Receptor
- Incretin System
- Appetite Regulation Signaling
- Neuroendocrine Signaling


