Cytokine Signaling
Cytokine signaling refers to the cell-to-cell communication network mediated by cytokines, a broad class of small signaling proteins that regulate immune responses, inflammation, and cellular coordination. In biological research, cytokine signaling is studied to understand how immune cells communicate, activate, suppress, or coordinate responses to internal and external stimuli.
Cytokines act by binding to specific cell-surface receptors, triggering intracellular signaling cascades that influence gene expression, cell differentiation, and immune system behavior.
Adaptive immunity refers to the specialized branch of the immune system that develops targeted responses to specific antigens through prior exposure. Unlike innate immunity, which provides immediate and non-specific defense, adaptive immunity is characterized by specificity, memory, and adaptability.
In biological research, adaptive immunity is studied to understand how immune cells recognize pathogens, generate antigen-specific responses, and retain immunological memory over time. This system is primarily mediated by T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes, which coordinate highly regulated immune signaling pathways.
⚠️ Research Disclaimer:
This content is provided strictly for educational and research purposes. No information on this page constitutes medical advice, dosing guidance, or instructions for human or animal use.
Research Context
In immunology and peptide research, cytokine signaling is examined to better understand:- Immune system activation and suppression mechanisms
- Coordination between innate and adaptive immunity
- Inflammatory response regulation
- Cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation pathways
- Immune signaling changes associated with stress, infection, or aging
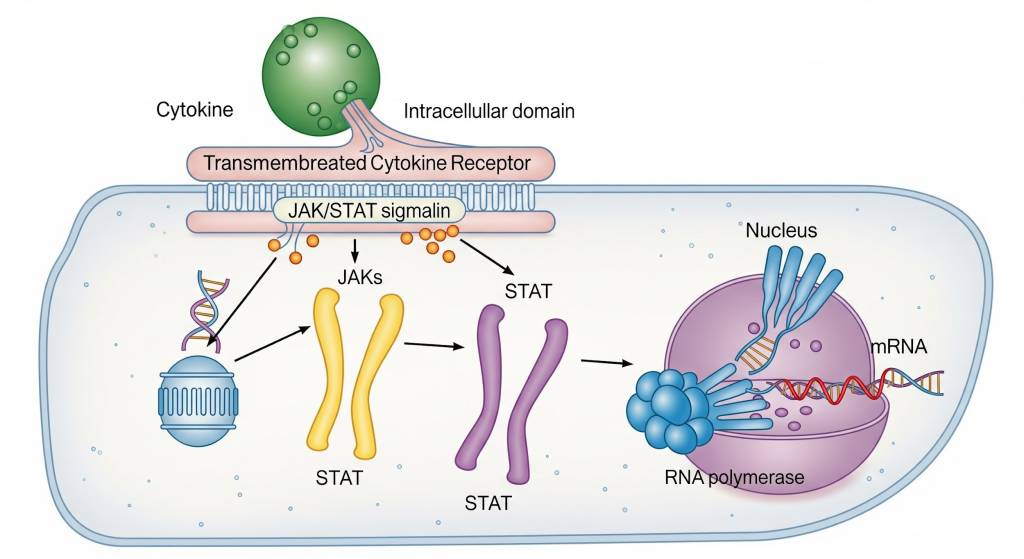
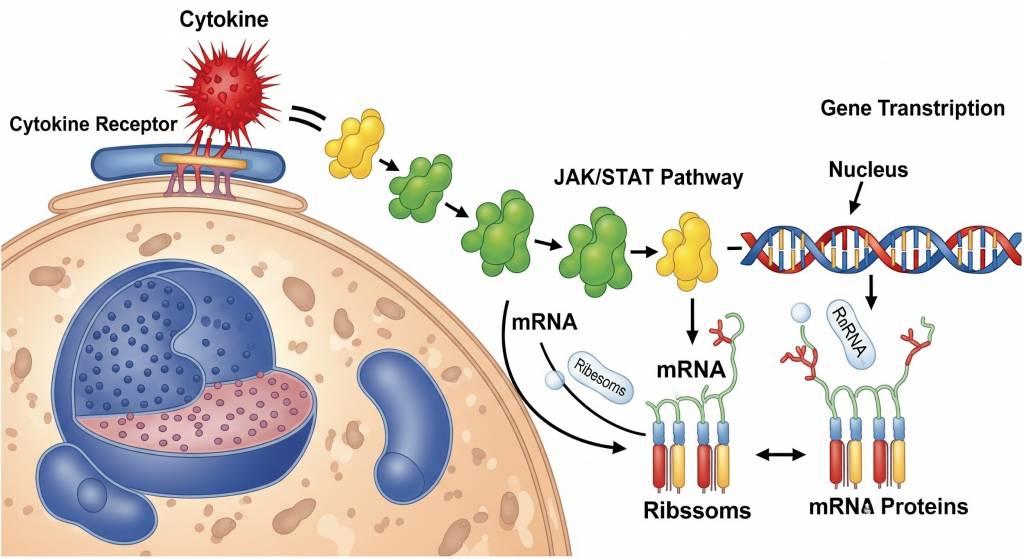
Components of Cytokine Signaling
From a research perspective, cytokine signaling typically involves:- Cytokines – signaling molecules released by immune and non-immune cells
- Cytokine receptors – cell-surface proteins that recognize specific cytokines
- Intracellular signaling cascades – such as JAK/STAT, MAPK, and NF-κB pathways
- Gene transcription responses – changes in cellular behavior driven by signaling activation
Cytokine Signaling and Immune Balance
Cytokine signaling plays a critical role in maintaining immune balance. Research explores how dysregulated cytokine signaling can lead to:- Excessive inflammation
- Impaired immune responses
- Chronic immune activation
- Altered tissue signaling environments
Relevance to Peptide Research
Cytokine signaling is highly relevant to peptide research because many peptides are studied for their ability to:- Modulate cytokine production or release
- Influence cytokine receptor signaling pathways
- Affect inflammatory signaling balance
- Coordinate immune cell communication
Related Research Compounds
Cytokine signaling is commonly referenced in research involving peptides such as:- Thymalin – studied in immune regulation and cytokine-associated signaling
- Thymogen – examined for immune gene expression and cytokine modulation
- Thymosin Alpha-1 – referenced in immune signaling and T-cell research
- LL-37 – studied for immune signaling and host defense interactions
- KPV – researched in inflammation-related signaling contexts
Related Glossary Terms
- Adaptive Immunity
- Innate Immunity
- Thymic Peptides
- Immunosenescence
- Host Defense Peptides


