Selank – Research Overview
Selank is a synthetic heptapeptide analog derived from the endogenous immunomodulatory peptide tuftsin, extensively studied in preclinical and laboratory research for its role in neuroimmune signaling, stress-response modulation, and cognitive pathway regulation. Due to its interaction with neurotransmitter systems and immune signaling pathways, Selank is frequently referenced in neuroscience research, anxiolytic pathway studies, and central nervous system–immune interface investigations.
This page provides a research-focused, educational overview of Selank, including its molecular classification, mechanism of action in research contexts, and primary areas of scientific investigation.
⚠️ Research Disclaimer:
This content is provided strictly for educational and research purposes. No information on this page constitutes medical advice, dosing guidance, or instructions for human or animal use.
Compound Overview
Selank is classified as a synthetic neuropeptide and immunomodulatory peptide analog, structurally derived from tuftsin, a naturally occurring tetrapeptide involved in immune signaling. In laboratory research environments, Selank is studied for its influence on central nervous system signaling, stress-related neurotransmission, and immune–neural communication pathways. Its dual relevance to both neurological and immune research places Selank at the intersection of neuroimmune regulation studies.Research Background & Classification
From a molecular research perspective, Selank belongs to a class of neuropeptide-based regulatory compounds designed to preserve endogenous signaling characteristics while improving stability and specificity. Researchers study Selank to explore how peptide signaling influences:- Anxiety and stress-response pathways
- GABAergic and monoaminergic neurotransmission
- Neuroimmune communication
- Cognitive processing and memory-related signaling
- Immune modulation via central nervous system pathways
Mechanism of Action (Research Context)
In laboratory research settings, Selank has been studied for its ability to modulate neurotransmitter signaling, particularly within GABA-related pathways, which play a role in stress regulation and emotional processing. Researchers analyze how Selank influences gene expression, neurotransmitter balance, and immune signaling mediators under controlled experimental conditions. Selank is also examined for its role in regulating cytokine-associated signaling, supporting research into neuroimmune balance and recovery mechanisms. All mechanisms are discussed strictly within a research context, without implication of clinical or therapeutic application.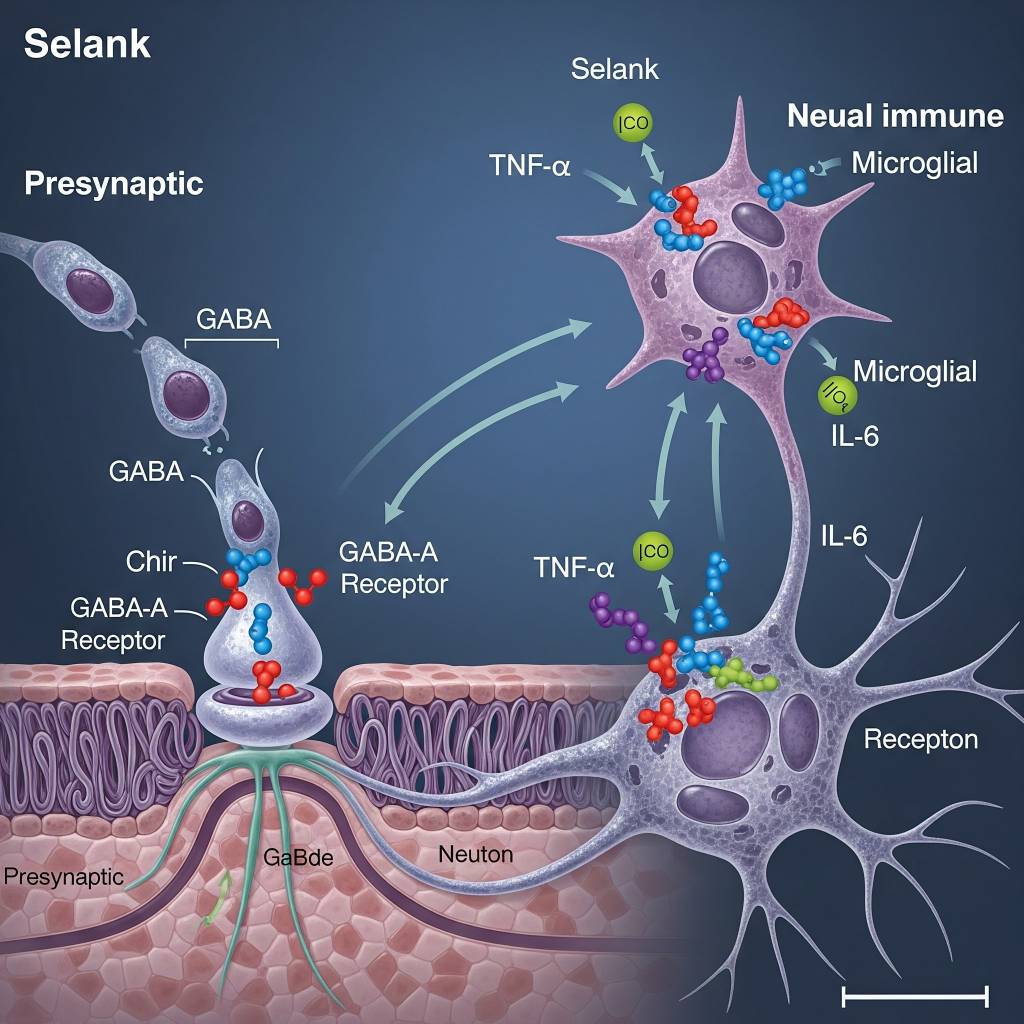
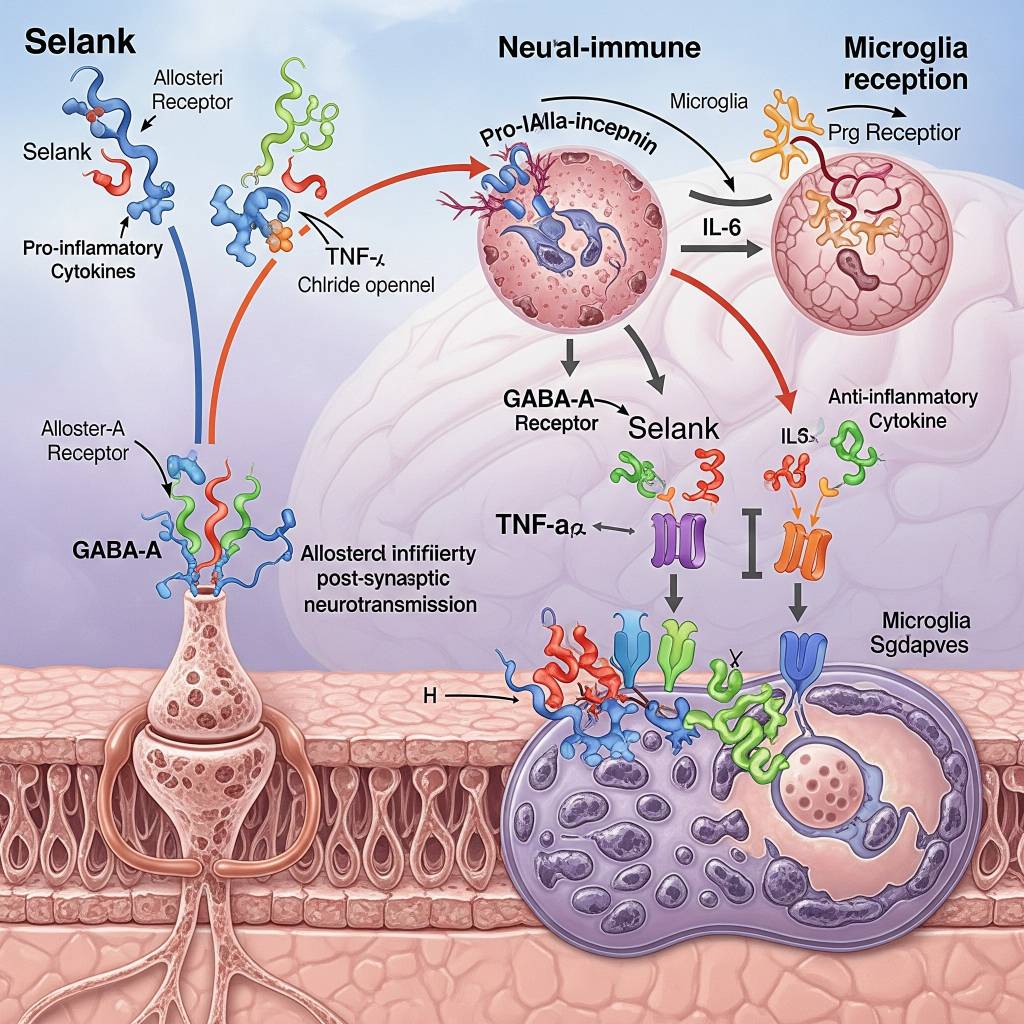
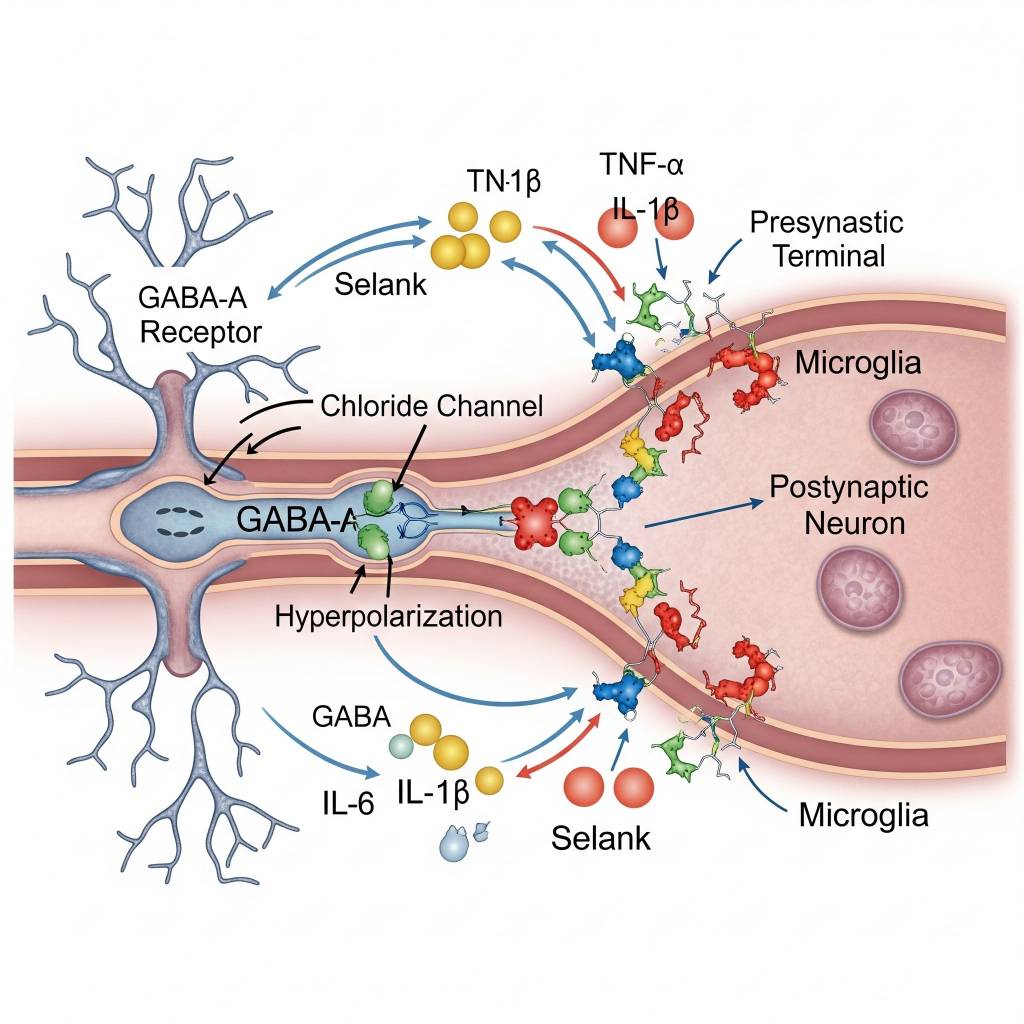
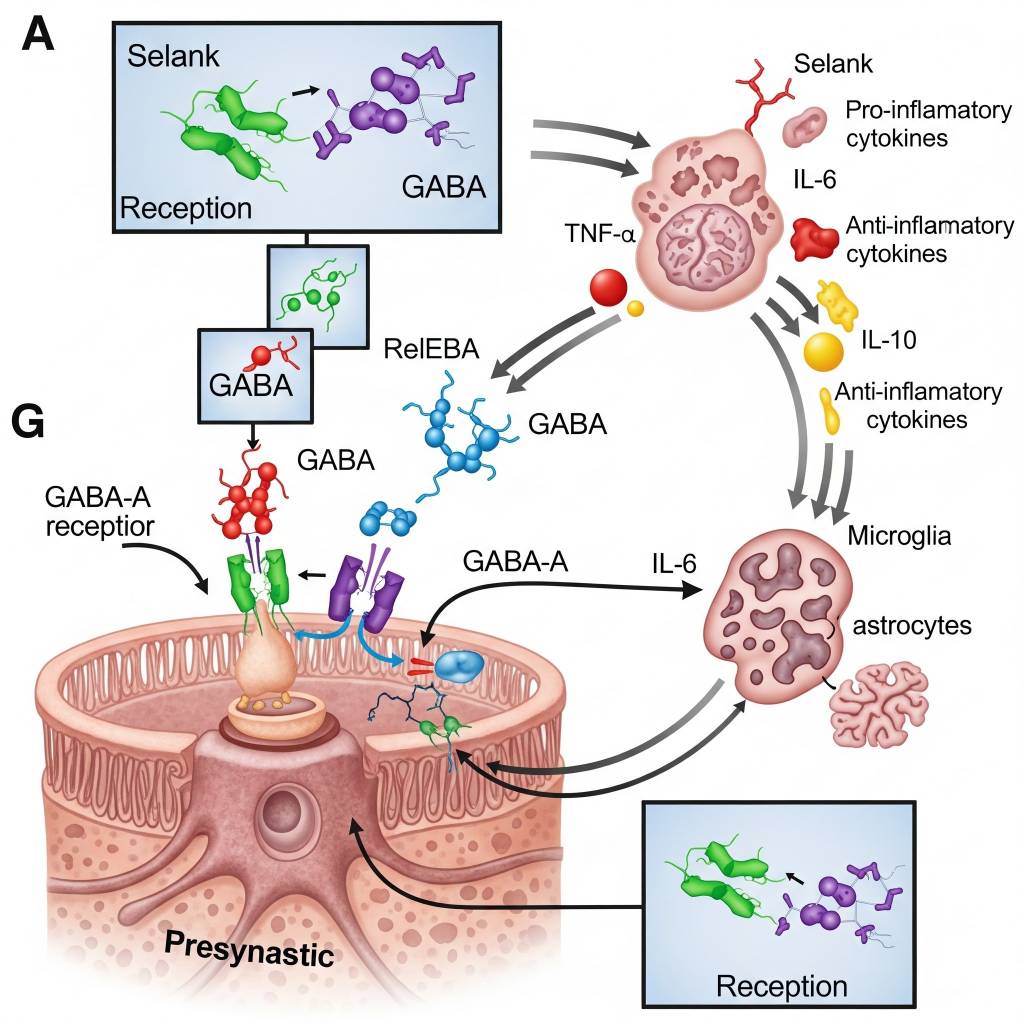
Areas of Scientific Research Interest
Selank has been referenced in scientific research related to:- Neuroimmune signaling pathways
- Stress and anxiety-related neuropeptide research
- GABAergic neurotransmission modulation
- Cognitive processing and memory signaling
- Central nervous system immune regulation
- Cytokine signaling and immune balance
- Behavioral neuroscience research models
- Neuroendocrine stress-response studies


