Follistatin-344 – Research Overview
Follistatin-344 is a glycoprotein-based peptide fragment derived from the larger follistatin protein that has been extensively studied in preclinical and laboratory research for its role in myostatin signaling inhibition, muscle cell regulation, and tissue growth pathway modulation. Due to its interaction with members of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) superfamily, Follistatin-344 is frequently referenced in muscle biology research, cell differentiation studies, and growth regulation signaling investigations.
This page provides a research-focused, educational overview of Follistatin-344, including its molecular classification, mechanism of action in research contexts, and primary areas of scientific investigation.
⚠️ Research Disclaimer:
This content is provided strictly for educational and research purposes. No information on this page constitutes medical advice, dosing guidance, or instructions for human or animal use.
Compound Overview
Follistatin-344 is classified as a myostatin-binding regulatory protein fragment, studied in laboratory research for its ability to interact with growth differentiation factors, particularly myostatin (GDF-8). In experimental environments, Follistatin-344 is examined to better understand how inhibition of myostatin-related signaling influences muscle cell growth, tissue differentiation, and protein synthesis pathways.
Its specificity for growth-regulating ligands makes Follistatin-344 a key compound in muscle growth signaling research and cellular hypertrophy pathway studies.
Research Background & Classification
From a molecular research perspective, Follistatin-344 belongs to a class of TGF-β binding proteins that regulate signaling by sequestering growth-inhibitory ligands. Researchers study Follistatin-344 to explore how modulation of these pathways affects:
- Myostatin and activin signaling
- Muscle cell differentiation and proliferation
- Satellite cell activation pathways
- Tissue growth and repair signaling
- Balance between anabolic and catabolic signaling
Follistatin-344 is widely cited in muscle development research, regenerative biology, and cell signaling regulation studies due to its central role in growth pathway modulation.
Mechanism of Action (Research Context)
In laboratory research settings, Follistatin-344 has been studied for its ability to bind and neutralize myostatin and related growth factors, thereby altering downstream SMAD-dependent signaling pathways. Researchers analyze how this interaction influences muscle fiber growth signaling, cell cycle progression, and protein synthesis regulation in controlled experimental models.
These mechanisms are explored strictly within preclinical and in vitro research contexts and are presented for educational purposes only, without implication of clinical or therapeutic use.
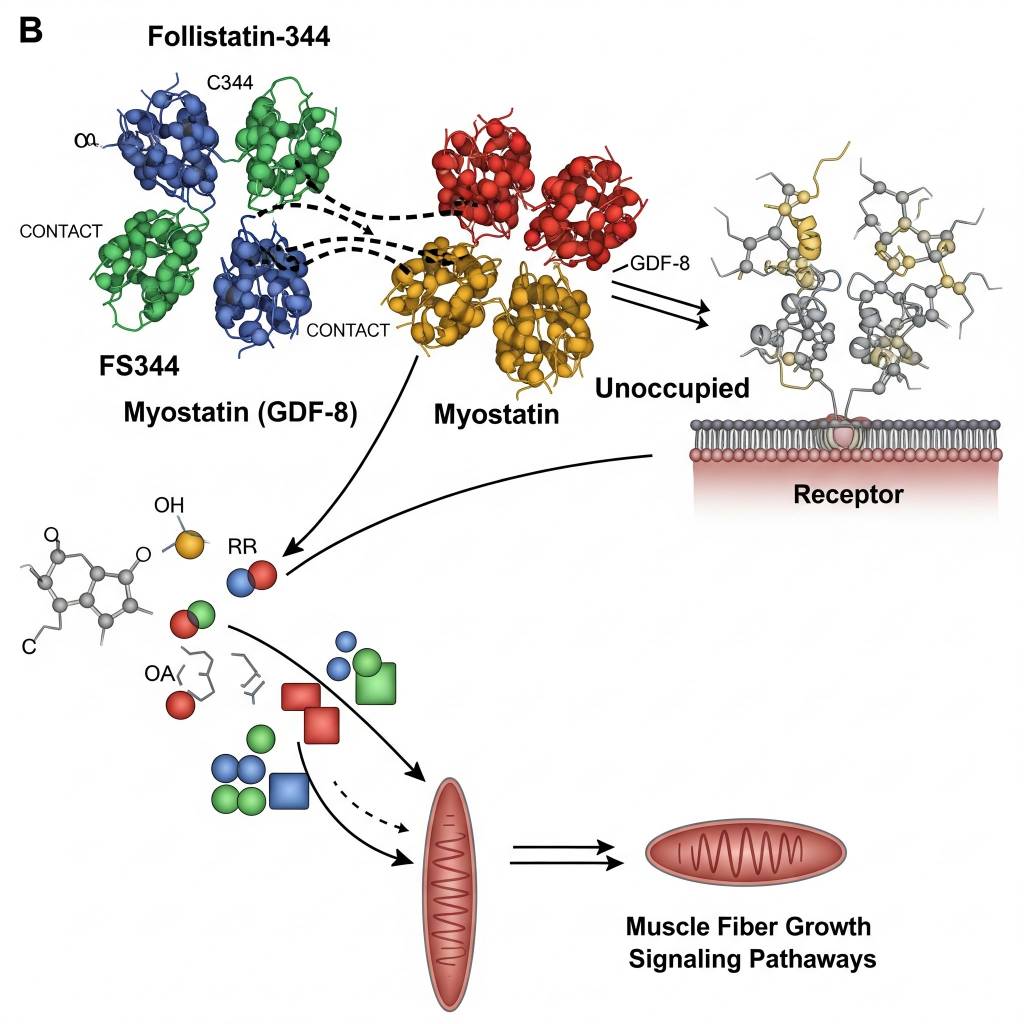
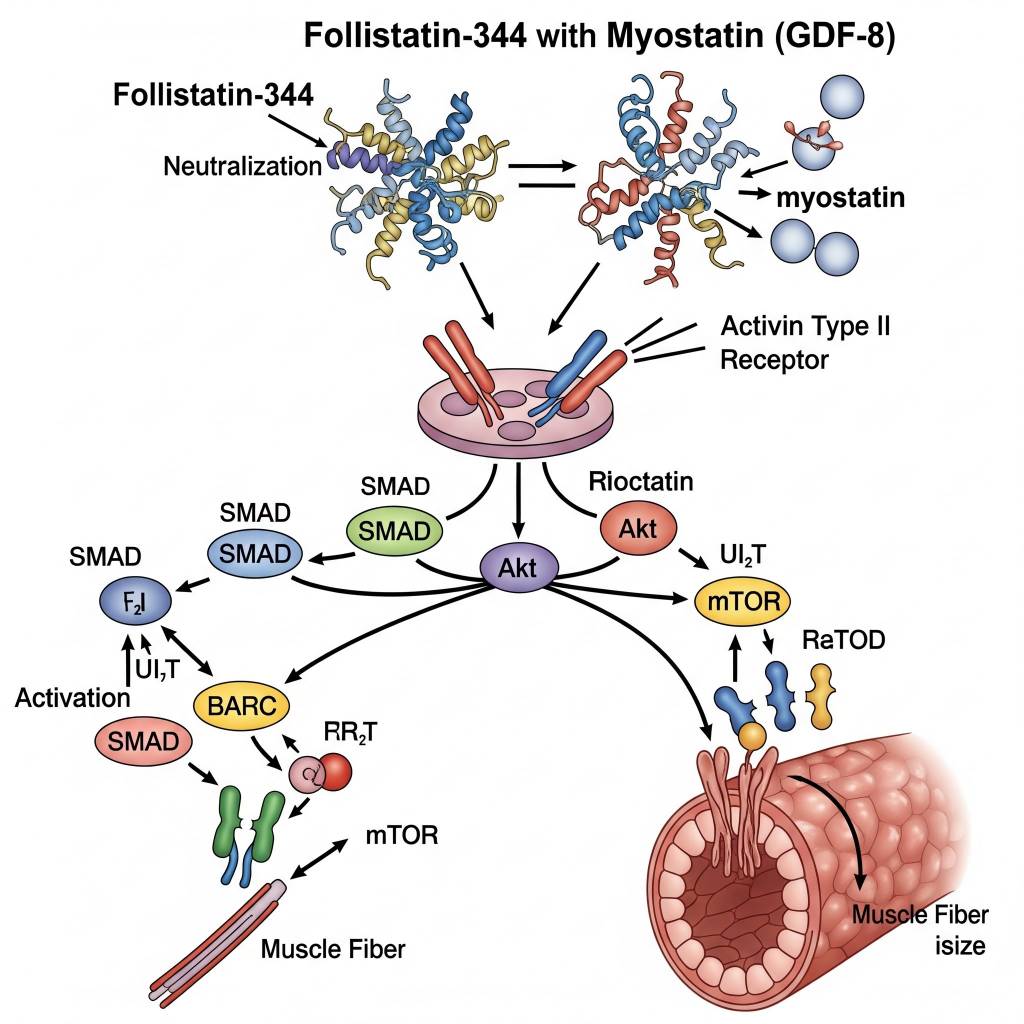
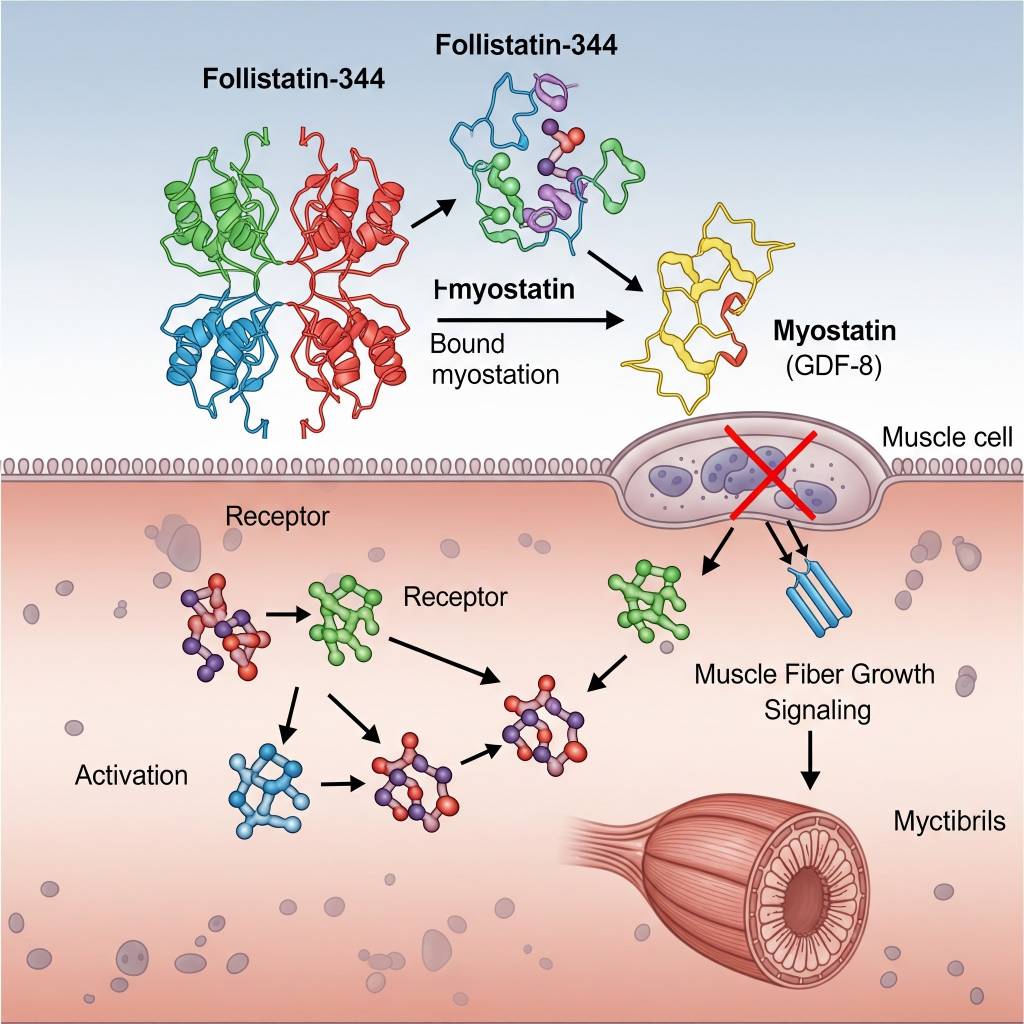
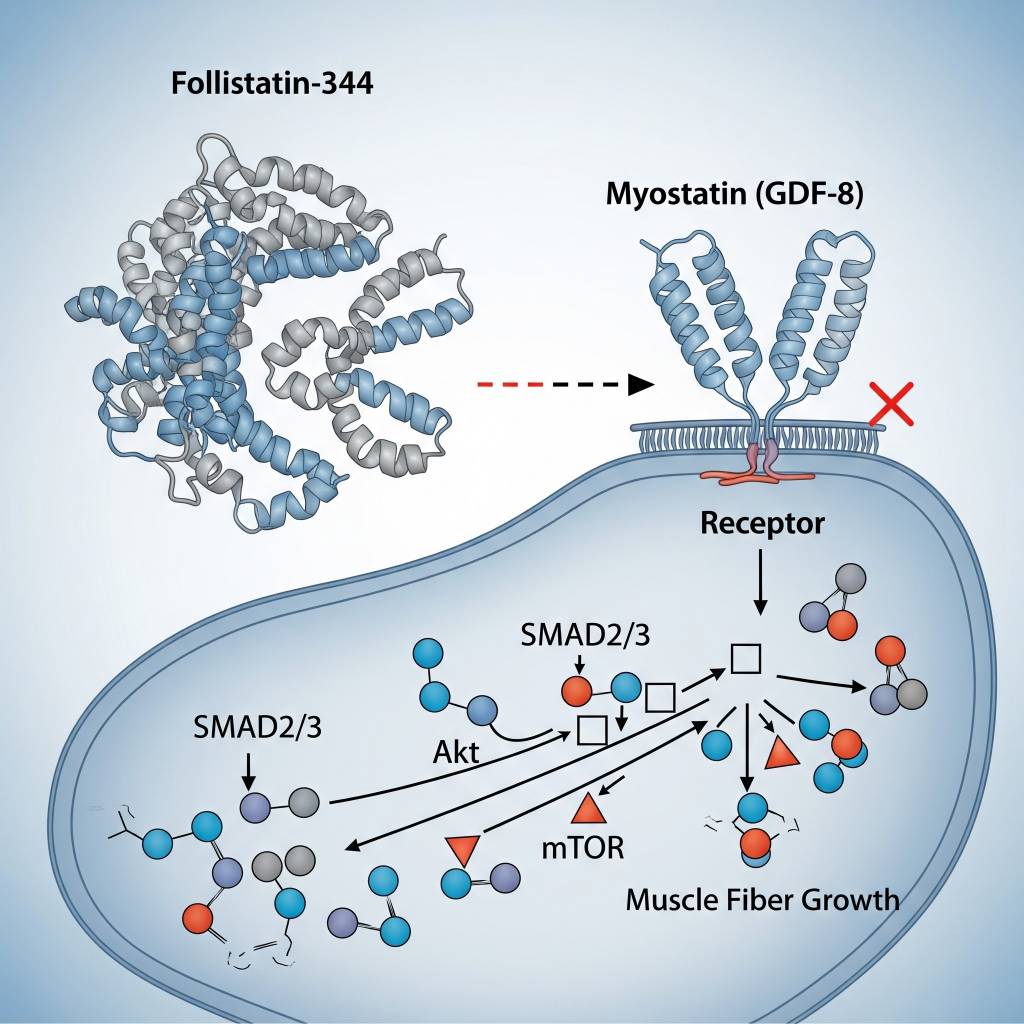
Areas of Scientific Research Interest
Follistatin-344 has been referenced in scientific research related to:
- Myostatin signaling inhibition
- Muscle hypertrophy pathway research
- TGF-β and activin signaling modulation
- Muscle cell differentiation studies
- Satellite cell activation research
- Growth regulation and tissue development pathways
- Structure–function analysis of regulatory proteins
These areas support broader investigation into how growth-inhibitory pathways are regulated at the molecular level in muscle and connective tissue research models.
Stability & Handling Considerations
In laboratory environments, Follistatin-344 is handled according to standard protein and peptide research protocols. Researchers consider factors such as temperature stability, solution composition, light exposure, and protein folding integrity when conducting experimental studies.
Proper handling and storage are critical for maintaining molecular activity and reproducibility during extended growth-pathway research experiments.
Research Context Notes
This overview is intended for educational and informational purposes for individuals studying molecular biology, muscle physiology, cell signaling, and growth regulation pathways. It does not replace peer-reviewed scientific literature, experimental protocols, regulatory documentation, or institutional research standards.
Researchers who have reviewed this compound overview may proceed to review available research compounds.


