Epitalon (Epithalon) – Research Overview
Epitalon, also known as Epithalon, is a synthetic tetrapeptide derived from Epithalamin, a peptide complex associated with the pineal gland. It has been extensively studied in preclinical and laboratory research for its role in cellular aging pathways, telomerase activity research, circadian rhythm signaling, and neuroendocrine regulation. Due to its unique association with aging and longevity-related molecular processes, Epitalon is frequently referenced in gerontology research, chronobiology studies, and cellular lifespan investigations.
This page provides a research-focused, educational overview of Epitalon, including its molecular classification, mechanism of action in research contexts, and primary areas of scientific investigation.
⚠️ Research Disclaimer:
This content is provided strictly for educational and research purposes. No information on this page constitutes medical advice, dosing guidance, or instructions for human or animal use.
Compound Overview
Epitalon is classified as a short synthetic peptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) studied for its ability to influence cellular regulatory pathways associated with aging and biological timing. In laboratory research environments, Epitalon is examined for its interaction with telomere-related signaling, pineal gland-associated pathways, and neuroendocrine communication systems. Its compact structure allows researchers to study precise molecular signaling effects in controlled experimental models.Research Background & Classification
From a molecular research perspective, Epitalon belongs to a class of regulatory peptides investigated for their role in genetic expression modulation and cellular longevity signaling. Researchers study Epitalon to explore how peptide-based signals may influence:- Telomerase-associated activity pathways
- DNA stability and chromosomal integrity
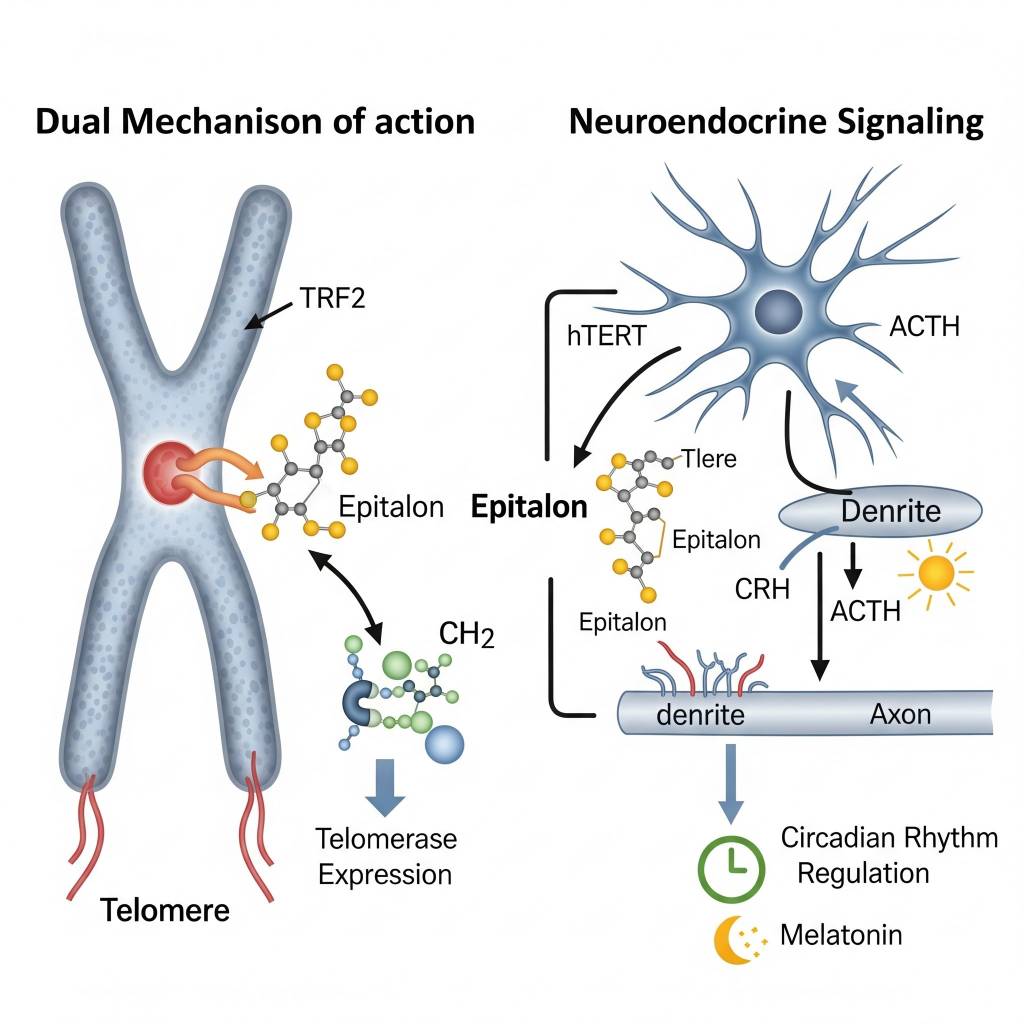
- Circadian rhythm regulation
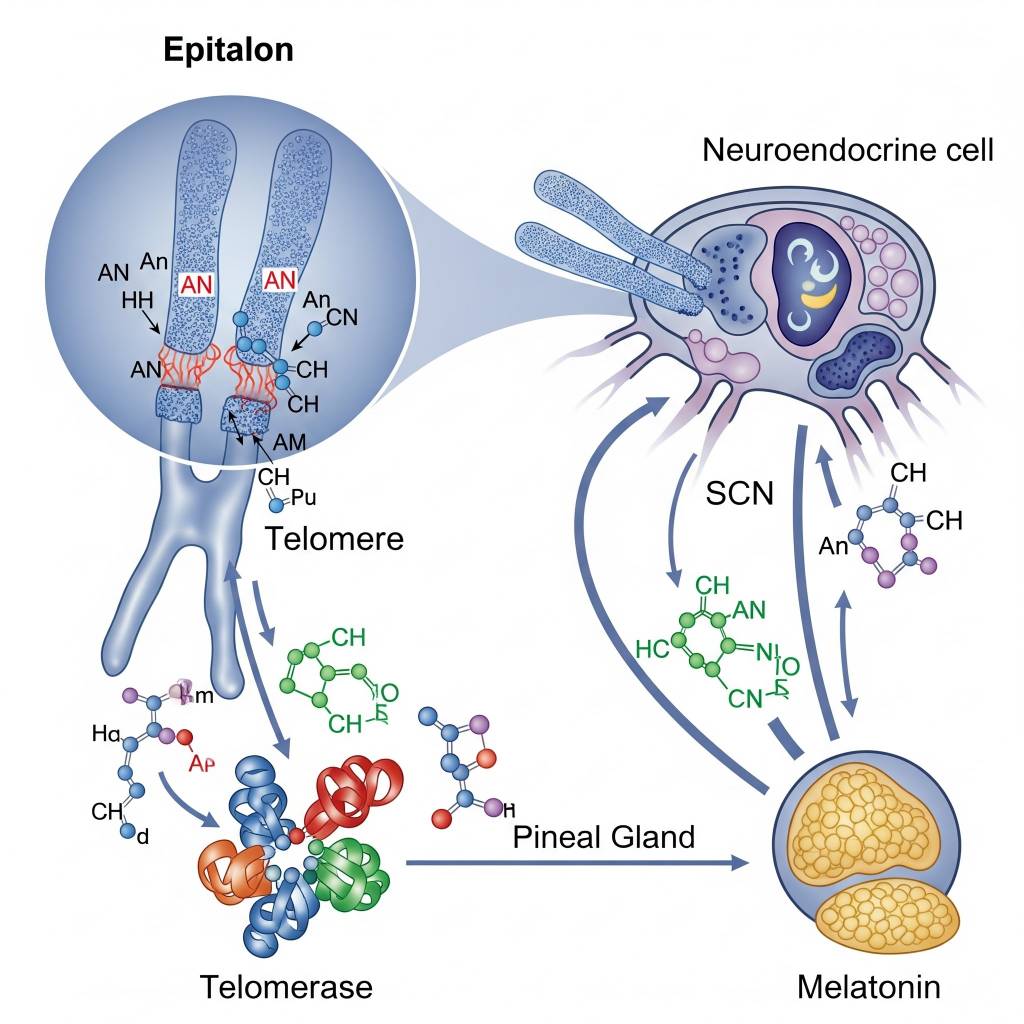
- Pineal gland signaling and melatonin-related pathways
- Neuroendocrine system coordination
Mechanism of Action (Research Context)
In laboratory research settings, Epitalon has been studied for its potential influence on telomerase expression signaling, which plays a role in chromosomal end-cap maintenance. Researchers also examine how Epitalon interacts with neuroendocrine signaling pathways, including those related to circadian rhythm regulation and hormonal timing signals. These mechanisms are investigated strictly within preclinical and in vitro research models and are presented for educational purposes only, without implication of clinical or therapeutic application.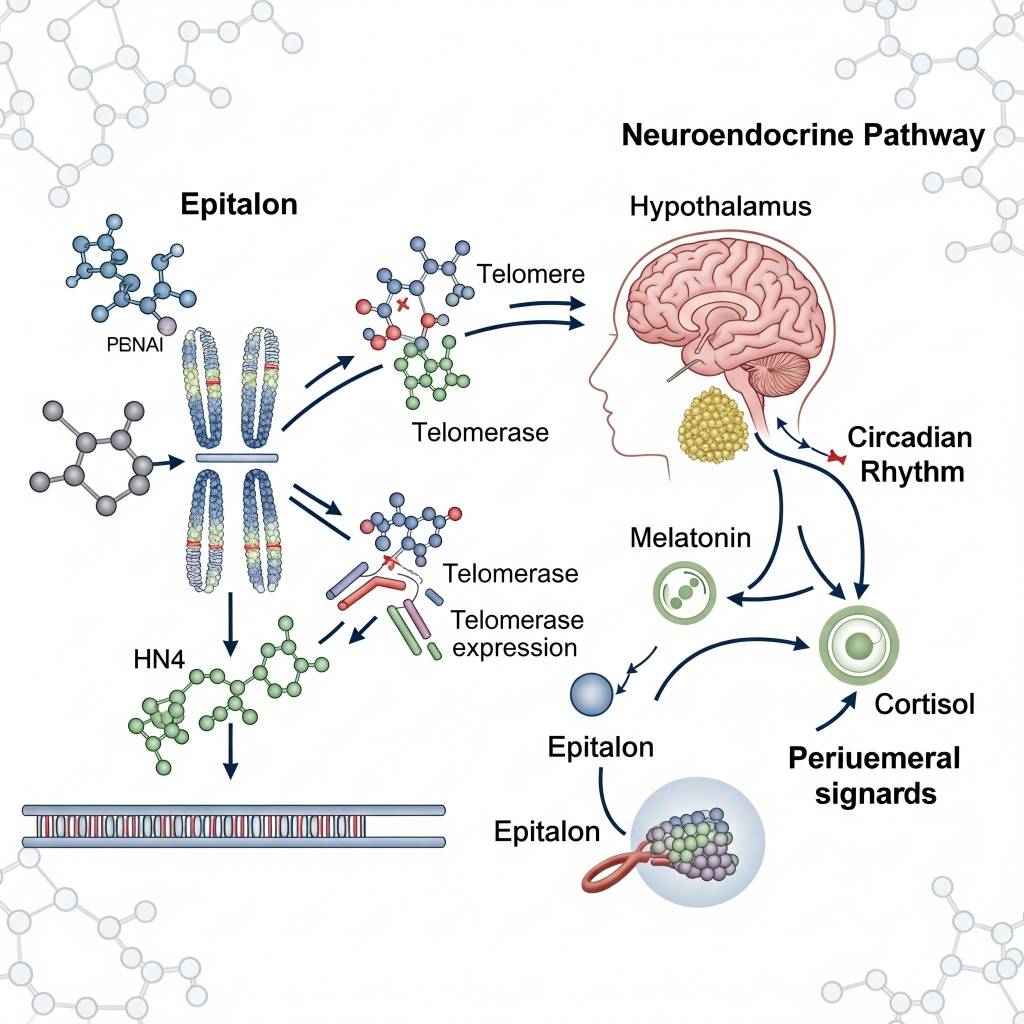
Areas of Scientific Research Interest
Epitalon has been referenced in scientific research related to:- Cellular aging and longevity signaling
- Telomerase-associated pathway research
- Chromosomal stability studies
- Circadian rhythm and chronobiology research
- Pineal gland peptide signaling
- Neuroendocrine regulation pathways
- Gene expression modulation by short peptides


