DSIP (Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide) – Research Overview
DSIP (Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide) is a neuropeptide that has been extensively studied in preclinical and laboratory research for its role in sleep-associated signaling, neuroendocrine regulation, and stress-response pathway modulation. Since its identification in sleep-related research models, DSIP has been frequently referenced in neuroscience studies, circadian rhythm research, and neuro-immune recovery investigations.
This page provides a research-focused, educational overview of DSIP, including its molecular classification, mechanism of action in research contexts, and primary areas of scientific investigation.
⚠️ Research Disclaimer:
This content is provided strictly for educational and research purposes. No information on this page constitutes medical advice, dosing guidance, or instructions for human or animal use.
Compound Overview
DSIP is classified as a nonapeptide neuropeptide, studied for its association with sleep architecture signaling and central nervous system regulation. In laboratory research environments, DSIP is examined to better understand how peptide-based signaling influences sleep cycles, stress physiology, and neuroendocrine communication. Because sleep plays a foundational role in immune recovery, metabolic regulation, and cellular repair, DSIP occupies an important position in recovery-focused research models.Research Background & Classification
From a molecular research perspective, DSIP belongs to a class of neuropeptides involved in homeostatic regulation. Researchers study DSIP to explore how neuropeptide signaling interacts with:- Sleep-wake cycle regulation
- Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis signaling
- Neuroendocrine stress response pathways
- Autonomic nervous system balance
- Neuro-immune communication
Mechanism of Action (Research Context)
In laboratory research settings, DSIP has been studied for its influence on delta-wave activity, a key component of deep sleep architecture. Researchers analyze how DSIP interacts with neurotransmitter systems, hormonal signaling pathways, and stress-associated molecular cascades. DSIP is also examined in studies exploring its relationship with cortisol regulation, melatonin-associated pathways, and neuro-immune recovery signaling. All mechanisms are discussed strictly within a research context, without implication of clinical or therapeutic application.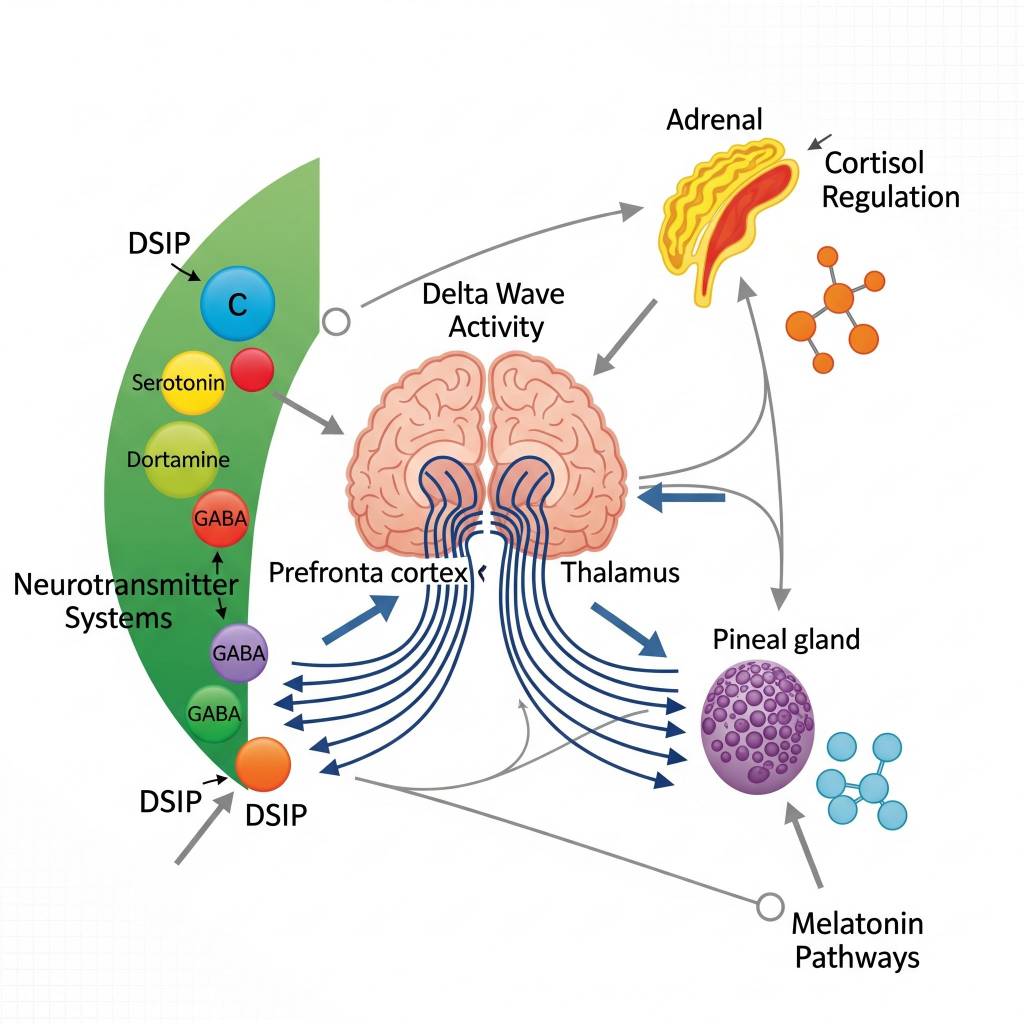
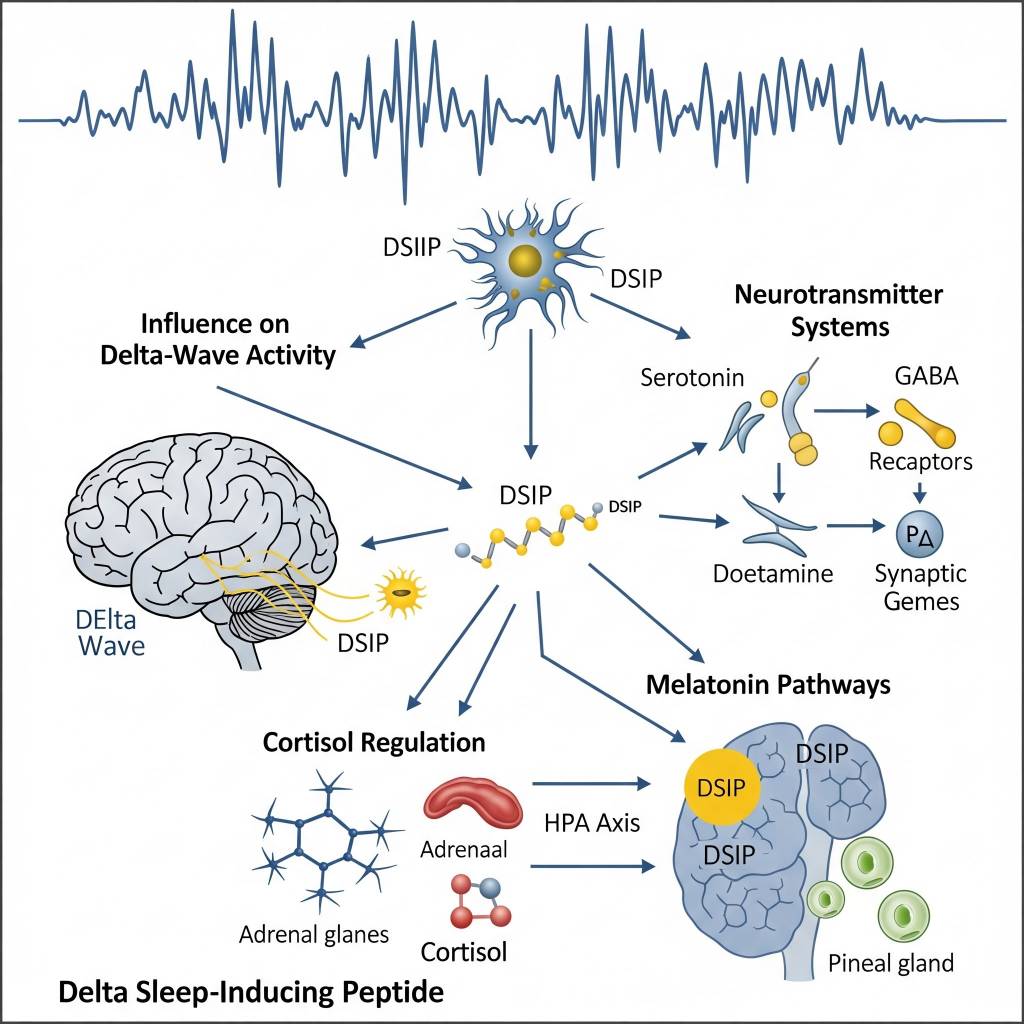
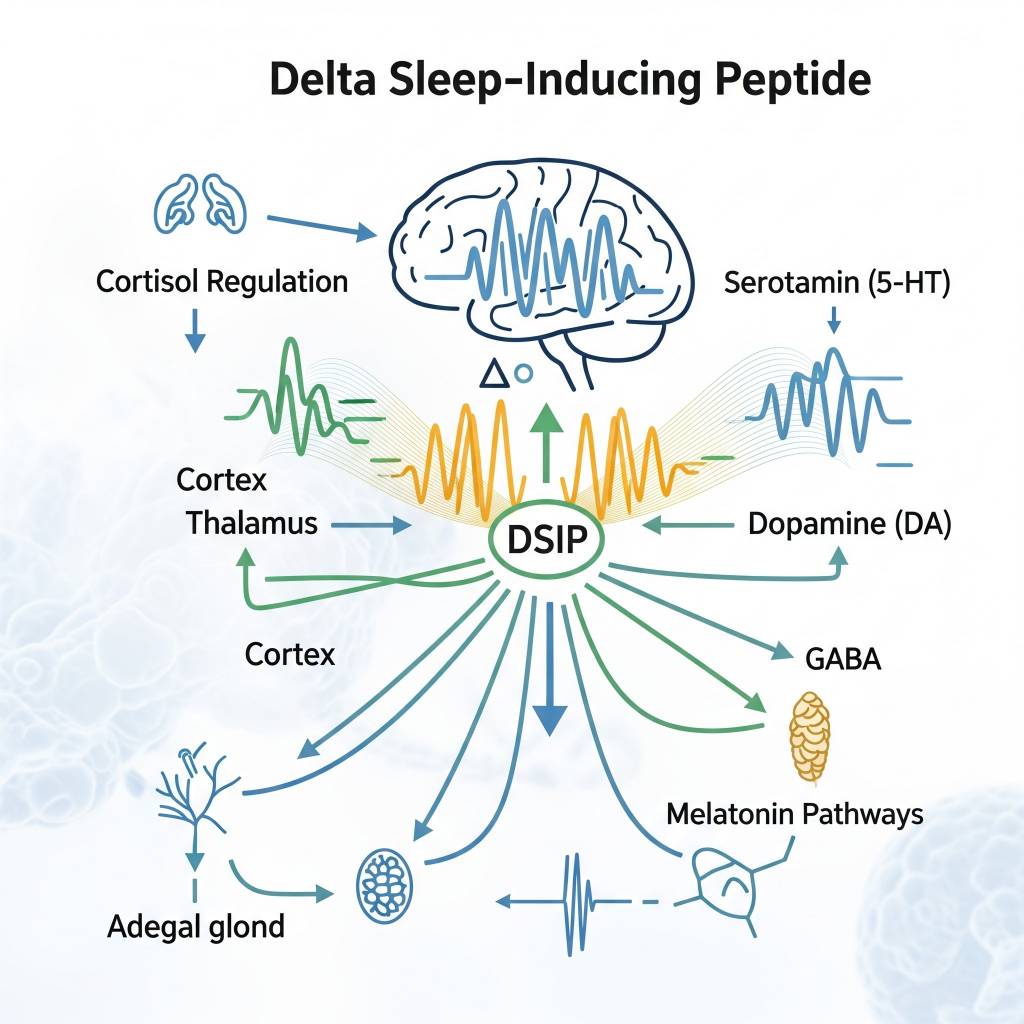
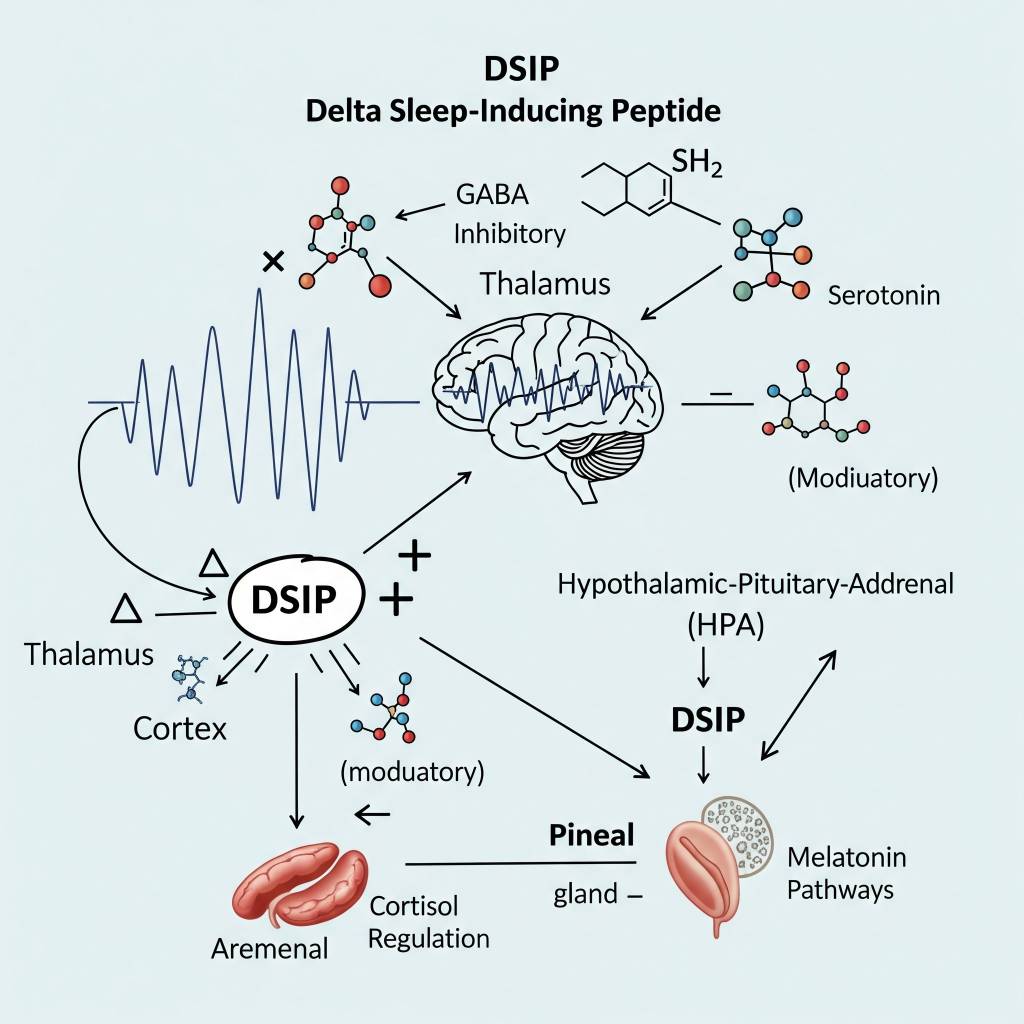
Areas of Scientific Research Interest
DSIP has been referenced in scientific research related to:- Sleep cycle and circadian rhythm research
- Delta-wave sleep signaling
- Neuroendocrine stress regulation
- HPA axis modulation studies
- Neuro-immune recovery pathways
- Central nervous system peptide signaling
- Homeostatic regulation research
- Sleep-associated recovery mechanisms


